The Challenge of Measuring Low IoT Currents
To maximize battery life, your product current draw must be kept to an absolute minimum. This requires that you use low power components and efficient techniques to de-energize components when they are not in use. You need sensitive measurement instrumentation to measure current levels as low as nA.
Determine the load current profile
It can be difficult to characterize the load current profile of a prototype IoT device, because you must measure the current in a wide range of operating states:
- sleep mode (from nA to µA),
- standby modes (from hundreds of microamps to tens of milliamps), and
- active states (from milliamps to amps), including short current bursts due to wireless transmissions
To accurately capture these widely varying load current levels, you need an exceptional measurement solution that includes:
- A wide current measurement range, from hundreds of nanoamps to amps
- The measurement speed to capture current pulses just a few microseconds wide
- A large memory buffer to store the prototype device’s current profile
Keithley’s DMM7510 7½-digit Graphical Sampling Multimeter is well-equipped to meet these demands, as it offers:
- pA current sensitivity
- 1 Msample/s sampling
- 27 M data points of memory
Determine the Average Current of an IoT Device
Measuring Ultra-Low Power in Wireless Sensor Nodes
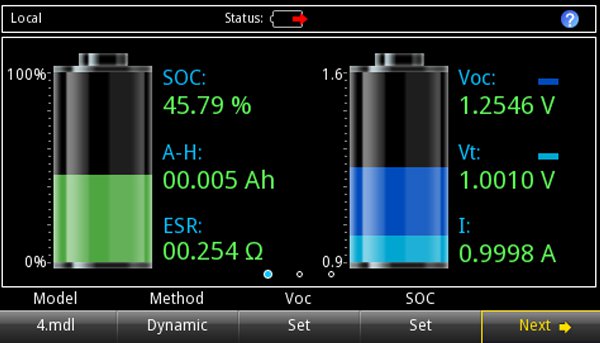
Simulate any battery type
How low can the battery voltage drop before your IoT device turns off? Gauging
battery performance at different stages of battery discharge is difficult, as it
requires instrumentation that can accurately simulate battery performance.
To address this, Keithley’s 2281S-20-6 Battery Simulator makes it easy to model
any type of battery. It allows you to efficiently test prototype IoT devices in any
battery state, with high repeatability to effectively estimate battery life. Combining
a 2281S-20-6 Battery Simulator with a DMM7510 Graphical Sampling Multimeter
will give you a complete solution for assessing power consumption and battery life
of your IoT prototypes.
How the 2281-S Emulates a battery

Model any type of battery
The final piece of the puzzle is to create a model for the battery that powers your
IoT device. Keithley’s 2450 or 2460 Graphical SourceMeter® Source Measure Unit
(SMU) instruments make it easy to create the model for the battery used
by your product.
A battery model-generating script operates the SMU instrument as a controlled
current load and derives the model parameters.
How to create a battery discharge model
Featured Content
Determine Load Current Profile
|
Simulate Any Battery
|
Model Any Type of Battery
|
|
DMM7510
|
|
|
 |
 |
 |
| The DMM7510 delivers a wide current measurement range, picoamp current sensitivity, high speed sampling, and a 27 million reading memory buffer to measure and store a prototype device’s current profile. |
Model any type of battery required to test devices efficiently and repeatably at any battery state. Also ideal for estimating battery life effectively is the combinination of a 2281S-20-6 with a DMM7510 to provide a complete solution for power consumption/battery life assessment. |
These SMU instruments can operate as a sensitive, electronic load to discharge a battery. In adddition, the SMUs can execute test scripts to monitor battery drain and create a model-generating script that lets them operate as a constant current load and derive the model parameters. |
- 1 Msamples/s current digitizer
- 100 pA – 10 A measurement range
- 27 million reading storage
- µA current triggering
- Touchscreen with graphical display
|
- 20 V, 6 A, 120 W capacity
- Simulates battery output using dynamic models
- Displays, Voc, SOC, Amp-Hr, and internal resistance
- Display visualization of battery state
x
|
- Constant voltage or constant current sourcing or sinking (four-quadrant operation)
- Up to 200 V, 7 A, 200 W
- Battery model application
|
Facing challenges in other power applications?
Characterization of Power Automated Parametric Test of Characterization and Troubleshooting
Semiconductor Devices Power Semiconductors of Power Conversion Designs

 KALİBRASYON LABORATUVARI
KALİBRASYON LABORATUVARI




